A smart building, also known as an intelligent building or connected building, refers to all the digital technology in a building that makes it possible to collect various types of data (related to occupancy rates, temperature, lighting, etc.) in real time, and make it available to all the related actors: occupants, operators, managers.
The main benefits offered by a smart building
As an innovative solution, a smart building allows several objectives to be pursued at the same time:
- Greater comfort for occupants
- Reduced running costs
- Predictive use management
Contributing to occupants’ comfort and mitigating climat change
A smart building helps combating global warming, in line with several EU Directives aimed at improving the energy efficiency of buildings and achieving a decarbonized building stock by 2050. It makes the use of shared space more efficient and helps to limit the escalation of unnecessary constructions. In this context, it also enables real-time monitoring of the indoor climate and air quality (CO2, temperature, relative humidity, TVOC) to improve occupant wellbeing.
Management of the building’s maintenance costs
Furthermore, it responds to economic issues since it is mainly used in a building in the operational (post-construction) phase, which alone accounts for around 80% of the total lifecycle costs of a building (average duration between 30 and 35 years). In this case, a smart building allows real-time monitoring of the condition of technical equipment.
Anticipating trends in occupancy and space utilization
Lastly, it facilitates adopting new work practices, since it allows, for example, the efficient implementation of teleworking and activity-based working in the office and guarantees efficient dimensions of space over time. As a result, businesses have greater organizational flexibility in and can guarantee healthy work conditions.
What are the benefits of a smart building for the company and its ecosystem?
The benefits are numerous and vary according to the different profiles in relation to the workplace, i.e.:
- The occupants
- The operators/technicians
- The managers/landlords
A smart building’s benefits for occupants
It guarantees the well-being and safety of users, because smart buildings increase the level of trust between employees/occupants and their workplace by empowering employees to various shared spaces (unassigned workstations, meeting and huddle rooms, bubbles, etc.) more effectively and in a more intuitive way. However, it will also prioritize employee satisfaction once more by, for example, making it possible to receive notifications of malfunctions in real time (touch button in the sanitary facilities, which triggers an intervention when pressed). Providing a pleasant work environment has become a key factor in talent acquisition and retention.
A smart building’s benefits for managers/landlords
Value retention of the commercial real estate asset because the smart building will allow us to know in a very precise and continuous manner the real occupancy rate of various spaces. This data enables workplace leaders to optimize space layouts and usage as well as to anticipate future needs. All the trends are now readily visible and available to organizations.
A smart building’s benefits for operators/technicians
Optimization of the management and maintenance of installations, because on the one hand the smart building facilitates increased productivity of the operational teams through digital tools displaying real-time information and also enhances the safety of these same employees, particularly during health crises, by providing them with adequate digital tools and up-to-date information (e.g. cleaning staff in hospitals receiving tailored work orders on digital floor plans with clear safety, hygiene, and sanitization procedures during the COVID-19 emergency).
How does a smart building work?
The smart building behaves like an open ecosystem that works on any building (tertiary or not) interconnected on one side to company software (ticketing, reservations, etc.) and on the other to third party building data feedback systems according to three possible integration approaches:
- The Internet of Things (IoT) is the interconnection between the Internet and physical objects, places and environments
- The Building Management System (BMS) is a computer system usually installed in large buildings or industrial facilities to supervise all the equipment installed there (lighting, air conditioning, etc.)
- A coexistence of the two elements IoT and BMS at the same site
Whatever the selected approach, the smart building allows the collection of this data and its transmission to a SaaS (cloud) software platform in an anonymous and secure manner, after which it is recovered by business applications, and also analyzed via dashboards intended for the experts concerned.

The IoT and the smart building
The IoT hardware used in smart buildings frequently includes sensors of various types (occupancy, humidity, CO2, touch command, door counter) based on a specific communication protocol (Sigfox or LoRa) that does not interfere with a company’s IT network. The vast majority of these sensors are wireless (offering several years’ autonomy), which makes the device discreet and mobile. The data originating from these sensors does not include any personal information since it relates to the work environment and not at all to individuals.
The BMS and the smart building
Some manufacturers are now offering access to information from their BMS systems, mainly for the latest models on the market that already support certain types of sensors. All the data relating to the supervised equipment (HVAC, lighting) as well as usage (occupancy, access control) are now accessible on the manufacturer’s cloud platform to which it is possible to interconnect via protocols such as API (Application Protocol Interface).
A smart building with IoT and BMS at the same time
Of course, it is possible to connect these two environments at the same site or building since they can be complementary. Indeed, it is perfectly possible to collect real-time data relating to lighting and air conditioning equipment from the installed BMS while gathering information relating to occupancy and temperature from wireless occupancy and comfort sensors (IoT). All this data is subsequently uploaded to a SaaS software platform that will make it available to all stakeholders involved in the corporate real estate chain.
The advantage of the IoT is the lower installation cost and the fact that it can be applied in any type of building (old or new) at whatever stage in the lifecycle (already built or not).
What are the next steps for the smart building?
Smart building with CMMS
This combination of in-depth knowledge of the building’s technical equipment (HVAC, lighting, etc.) and the actual use of the rooms (occupancy of meeting rooms, use of sanitary facilities, etc.) will lead to companies in charge of maintenance and upkeep redefining their core business by offering more responsive maintenance, which is now becoming predictive, aimed at improving user comfort on the one hand and optimizing the life of the installations on the other. A smart building supported by a CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) thus allows us to define a new-generation tool called Smart CMMS.
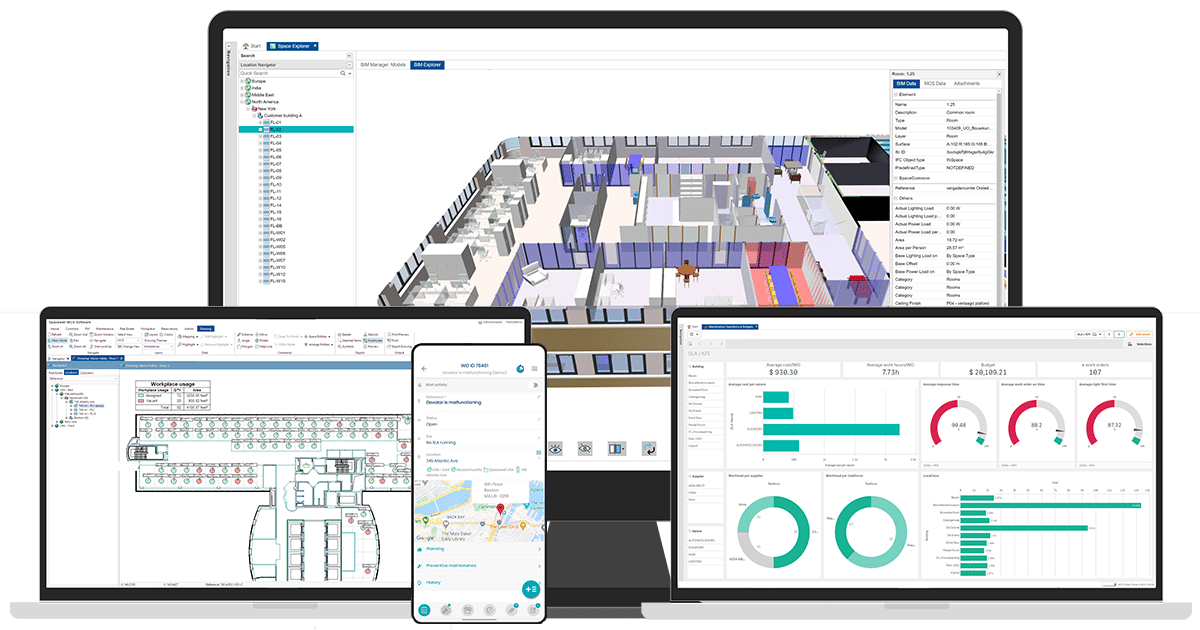
Smart building with BIM
The use of (3D) Building Information Modelling (BIM) in the Management-Operation-Maintenance phase of a building is already a remarkable step forward in itself and the addition of the smart building naturally reinforces the digitization of a building’s entire life cycle. The end-to-end digital vision, from design to construction, followed by continuous monitoring of usage and resource use/consumption becomes the basis for collaborative exchanges between all actors in the building.
How are smart buildings influencing future constructions?
The end-to-end digital vision described above constitutes a virtuous circle, as it will make it possible to influence the design of future constructions. In fact, all the on-site information originating from the smart building allows us to establish whether a particular architecture/configuration of a type of space is favoured by the occupants or to be avoided because it is never occupied, if a type of equipment malfunctions more frequently in relation to its storage location, etc. All the data from the smart building will be put to good use by architects to facilitate the design of a future site based on these valuable elements.
Frequently asked questions
The main advantages of the smart building include the following:
– It contributes to the comfort and working environment of the occupants.
– It enables you to manage building maintenance costs, particularly through predictive maintenance.
– It helps you to anticipate occupancy and usage patterns of the property.
Smart buildings rely on data feedback. A smart building with IoT (Internet of Things) and BMS (Building Management System) is the most complementary solution.







